CASE20250514_001
Attempted Endovascular Aortic Valve Replacement, Aortic Valve Reimplantation
By Rustam Abdrakhmanov, Konstantin Zavialov, Sergei Blagodarov, Albert Gilemkhanov, Teymur Ibragimov
Presenter
Konstantin Zavialov
Authors
Rustam Abdrakhmanov1, Konstantin Zavialov1, Sergei Blagodarov1, Albert Gilemkhanov1, Teymur Ibragimov1
Affiliation
Clinic of Bashkir State Medical Univercity, Russian Federation1,
View Study Report
CASE20250514_001
TAVR - Non-femoral TAVR
Attempted Endovascular Aortic Valve Replacement, Aortic Valve Reimplantation
Rustam Abdrakhmanov1, Konstantin Zavialov1, Sergei Blagodarov1, Albert Gilemkhanov1, Teymur Ibragimov1
Clinic of Bashkir State Medical Univercity, Russian Federation1,
Clinical Information
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Patient A, 82 years old.
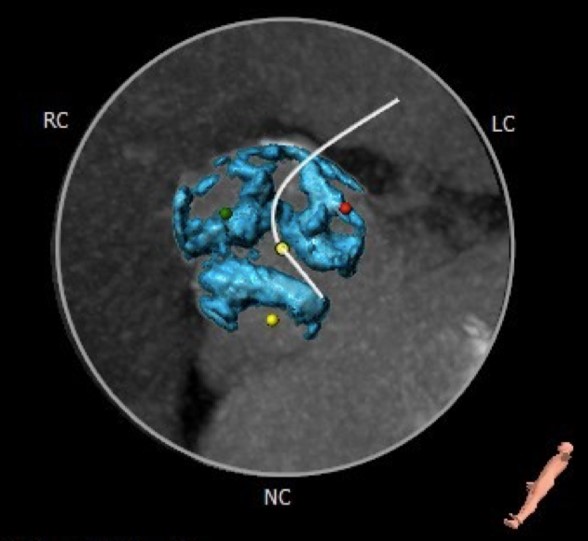
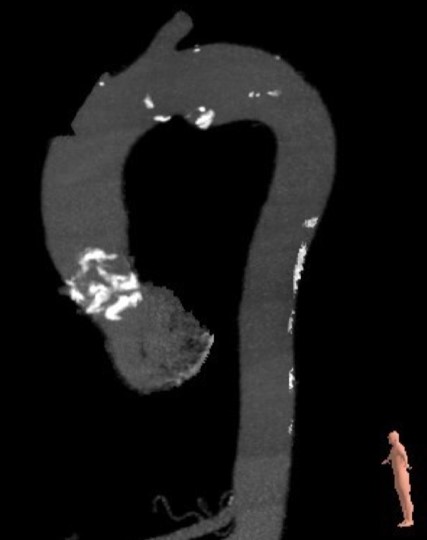


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Echocardiography: EF 63%. Aortic valve FR- 2.1 cm, leaflets are compacted, Ca 3 stage, mobility is limited GD 141/100 mmHg GD of the outflow tract- 3/2 Vmax- 594 cm/s AVA (VTI)- 0.4 cm2. Mitral valve leaflets are compacted, Ca of the fibrous ring, mobile. GD 7/3 mmHg GD 4.0 mmHg. There is no pericardial effusion. Dopplerography: Mitral regurgitation 2 (+) VC- 0.41 cm Aortic regurgitation 1 (+) Tricuspid regurgitation 2-3 (+). VC- 0.3 cm Calculated pressure in the right ventricle 44 mmHg.
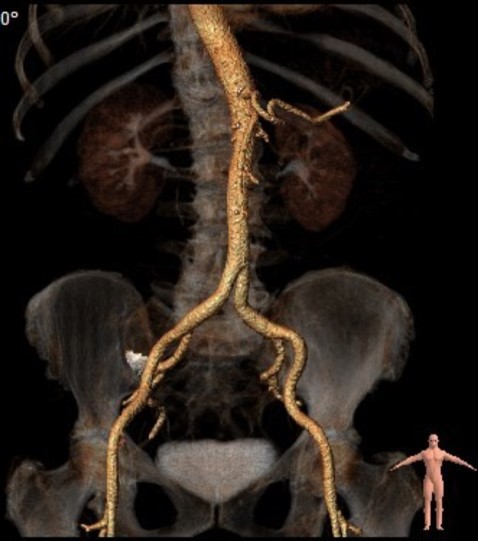

Relevant Catheterization Findings
The aortic valve opened stepwise under X-ray control and with contrast from an automatic injector. The valve delivery system folded and removed stepwise. Control performed using transthoracic echocardiography and contrast from a C Pig 6Fr 125 cm catheter.
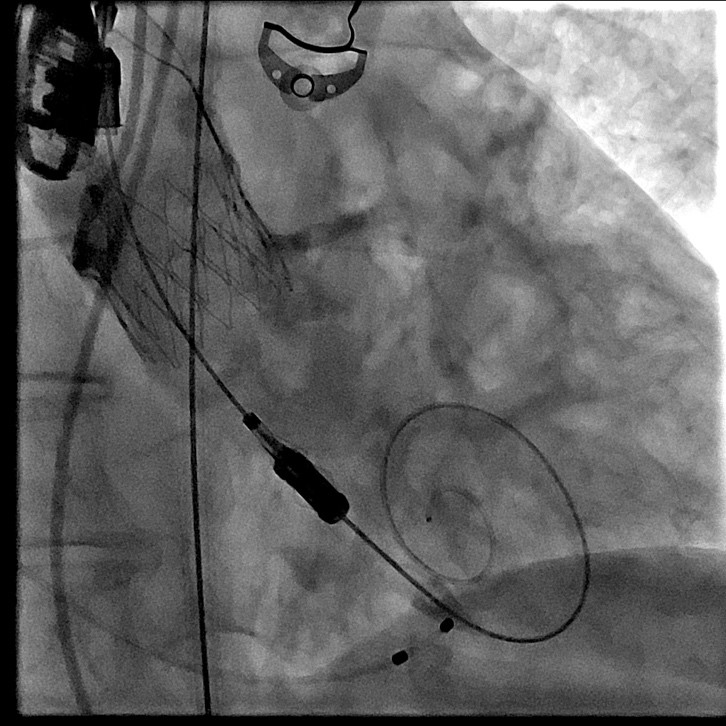

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
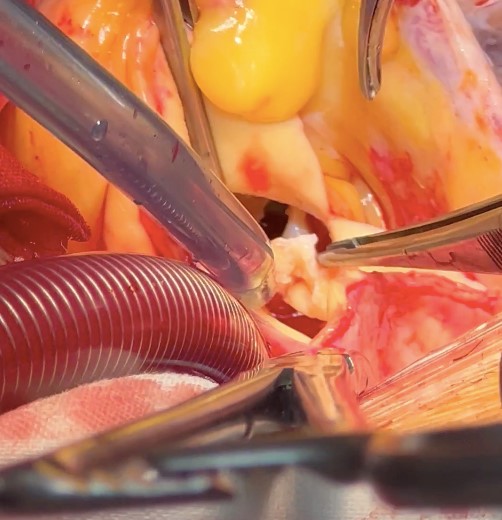
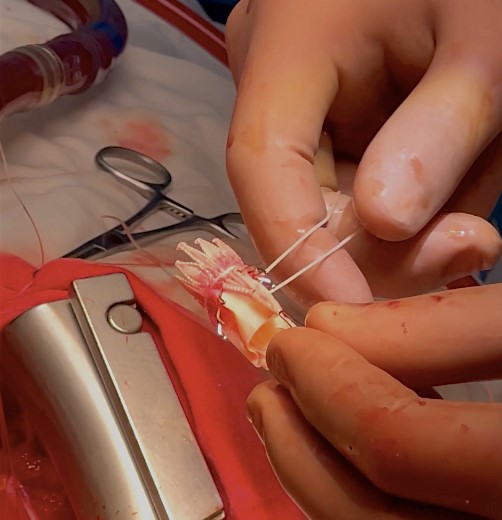
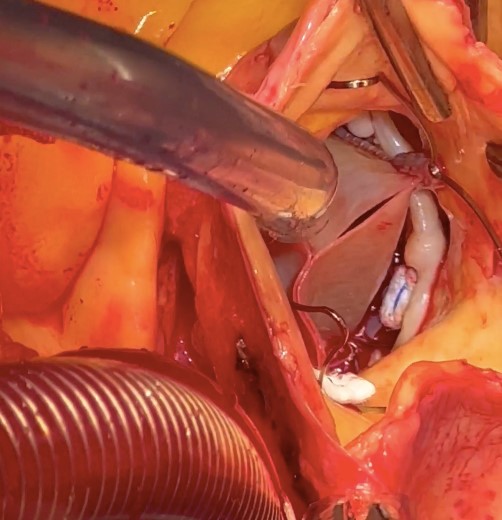
Sternotomy. Pericardiotomy. During revision, the heart is enlargedmainly due to the left sections, the ascending aorta is not dilated. Theprosthesis frame palpated in the ascending aorta up to the brachiocephalictrunk. Cannulation of the aorta into the arch. Connection of the artificialheart pump according to the scheme - "Aorta-Right atrium" using atwo-stage venous cannula. Longitudinal aortotomy. The prosthesis is in thelumen of the aorta. The prosthesis carefully removed. Clamp on the aorta. The prosthesis immersed in ice. Antegrade cardioplegia into the orificesof the coronary arteries. Drainage of the left sections of the heart - theorifice of the right superior pulmonary vein. Asystole. During revision: theaortic valve is tricuspid with pronounced calcification of the valves.Marginal decalcification of the left and right coronary cusps. Theprosthesis frame has become flexible, the folded prosthesis is implanted intothe aortic ring.The prosthesis arches fixed to the ring and to the aorta on Teflongaskets on three sides. The prosthesis cusps function normally.



Case Summary
1. Stay brave and curious.

